Preserving jellyfish
for DNA analyses
(From: Dawson et al. 1998)
Equipment:
1. Sterile syringes, forceps, dissecting scissors, or razor blades
2. A way of cleaning the sampling tools if they are not disposable
(e.g. flaming metal objects after dipping in ethanol, or a good rinse and wipe
dry)
3. Vials containing 1-2 ml of preservative (DMSO+NaCl or ethanol [70% to 95%;
>90% preferred]; will be provided upon request).
4. Chest of ice (in the
field); ice, refrigerator, or freezer (at lab/home, separate from food).
5. Protective gloves (latex,
rubber)
Procedure A - sampling
gut or gonad:
1. Collect medusae.
2. Starve the medusae for as long as possible.
3. Using a clean syringe, flush the guts with tapwater. Repeat several times
to displace any debris from the guts.
4. Using the same syringe (or other tool), suck up (tear or cut) about 0.1-0.2
ml of gastric and/or gonadal tissues.
5. Preserve the tissue in one vial of preservative. (Make sure
there is excess preservative; guard against diluting the preservative with too
much water.)
6. Label the vial and put it on ice. Store on ice, in a freezer or refrigerator
until the samples are shipped or analyzed (separate from food).
7.
Clean tools and gloves, repeat for the next sample.
Procedure B (quicker
alternative) - sampling oral arms or bell margin:
1. Collect medusae.
2. Flush the oral arms or bell margin with tapwater. Repeat several times to
displace all debris.
3. Using clean forceps/scissors, cut a half-small-fingernail sized piece of
tissue from the oral arm or bell margin. (It may be possible
to do this simply by holding the tissue across an open vial of preservative
and closing the lid.)
4. Preserve the tissue in one vial of preservative. (Make sure
there is excess preservative; guard against diluting the preservative with too
much water.)
5. Label the vial and put it on ice. Store on ice, in a freezer or refrigerator
until the samples are shipped or analyzed (separate from food).
6. Clean tools
and gloves, repeat for the next sample.
Notes:
DMSO+NaCl solution is 20% DMSO, 0.25M disodium-EDTA, and NaCl to saturation, pH 7.5 (Seutin et al. 1991); the pH of this solution must be >8 for the EDTA to dissolve, and warming promotes dissolution of NaCl. Sterilized by autoclaving prior to use.
100% ethanol is diluted to 80% (or greater) using purified drinking water (tapwater generally will suffice).
An important concern when sampling is to avoid contaminating the sample with tissues from other species (e.g. food) or with tissues from other individuals (see steps 2, 3, 7 in procedure A; steps 2, 3, 6 in procedure B).
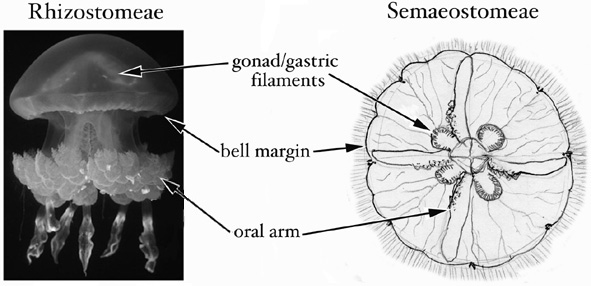
Both procedures A and B are designed to sample as much tissue and as little mesoglea (the 'jelly' of jellyfish) as possible. A third approach, not described above, is simply to preserve the whole animal, or a simple fraction thereof, if it has been cleared of potential contaminants and is small enough to fit easily into a vial with excess preservative (i.e. it is approximately <1 cm bell diameter). The figure below indicates the tissues best suited to sampling. The same methods also can be used to preserve coronate jellyfish and stauromedusae for DNA analyses.

Safety information:
The chemicals in the DMSO+NaCl
preservative are quite benign, being mostly water and table salt (see above).
However, this information accompanies the two main chemicals.
1. DMSO (liquid,
20% of preservative by volume). "Causes skin irritation. Causes digestive and
respiratory irritation. May cause severe eye irritation and possibly injury.
May be absorbed through the skin. For eye contact, flush with water for 15 minutes
and get medical aid immediately. For skin contact, flush with water and get
medical aid. If ingested, do not induce vomiting and get medical aid immediately.
If inhaled, remove to fresh air and get medical aid immediately."
2. EDTA (powder,
@ 0.25M in preservative). "May cause irritation. For eye contact, flush
with water and get medical aid. For skin contact, get medical aid if irritation
occurs or persists. If ingested, give 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water and get medical
aid. If inhaled, get medical aid if cough or other symptoms appear."
Ethanol is highly flammable. It should be kept away from naked flame and sources of heat at all times. It should not be transported except in small quantities packaged appropriately (check protocols for transporting hazardous substances).
Jellyfish stings can be at best uncomfortable and at worst lethal. Jellyfish must be handled with the utmost care, and protective clothing and gloves worn at all times. If you have any doubts, do not touch them. Ask for expert advice.
For
FREE DNA sequencing
of any scyphozoan ...
Airmail preserved
samples at room temperature to:
Dr. Michael Dawson
School of Natural Sciences
University of California at Merced
5200 North Lake Road
Merced, CA 95340
USA
Click here for details.